Activation Functions
What are activation functions and why do we need them?
Activation functions define the output of the neurons for a set of inputs. In a broader sense, activation functions prevent linearity i.e. if we take a linear activation function, we end up with an output, which is a linear function irrespective of whether our data is linear or not linear.
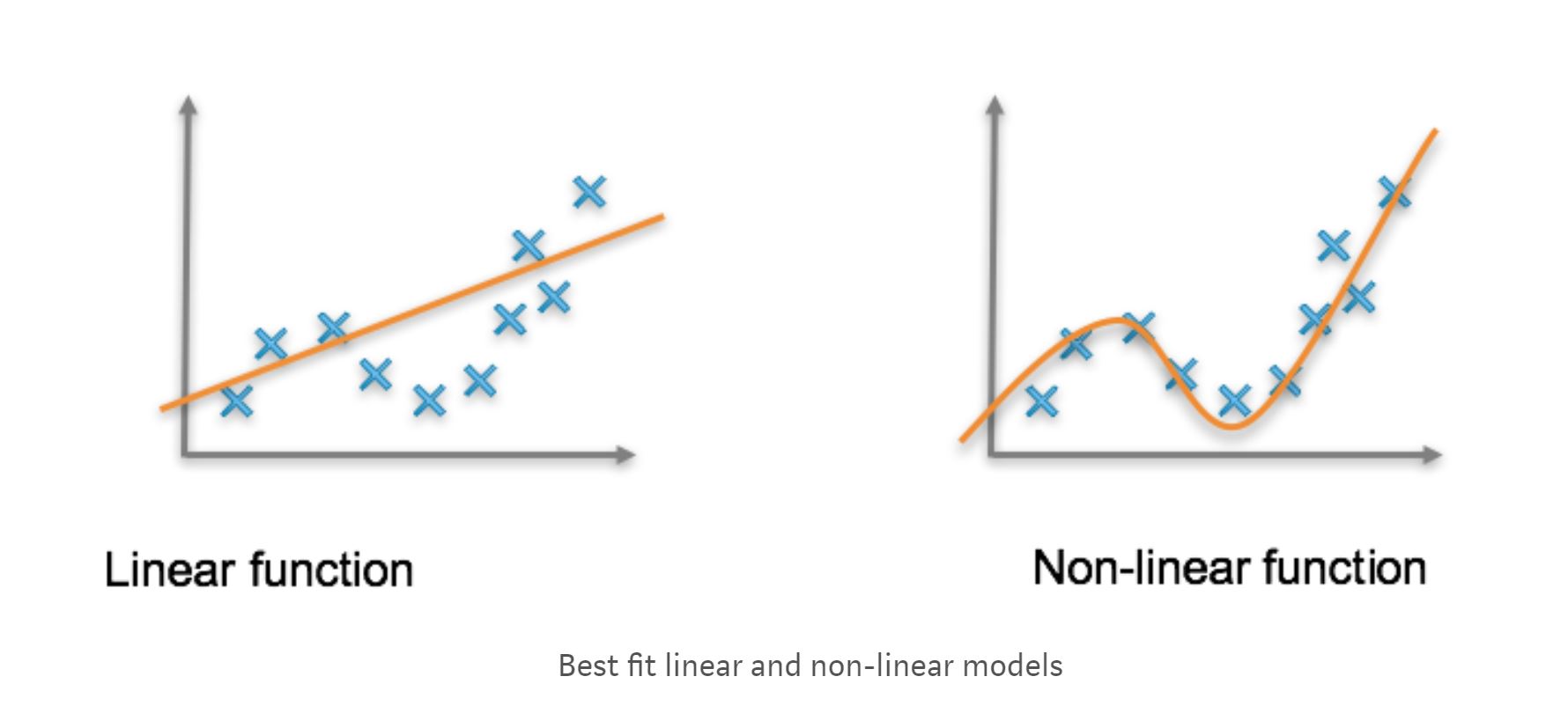 To introduce non-linearity in our dataset we use activation functions. For peeps more interested in the technicalities, activation functions counter the problem of vanishing and exploding gradients which arise as a result of the deeper networks where the value of derivative terms is usually less than 1 . When we multiply the derivative terms successively, the gradient becomes smaller and eventually vanishes. Otherwise, when the derivative terms are greater than 1, their multiplication leads to gradients that tend to infinity. Activation functions counter this problem by limiting the value of the gradients. Such results can be achieved with the help of different mathematical functions, used for neural network computing.
To introduce non-linearity in our dataset we use activation functions. For peeps more interested in the technicalities, activation functions counter the problem of vanishing and exploding gradients which arise as a result of the deeper networks where the value of derivative terms is usually less than 1 . When we multiply the derivative terms successively, the gradient becomes smaller and eventually vanishes. Otherwise, when the derivative terms are greater than 1, their multiplication leads to gradients that tend to infinity. Activation functions counter this problem by limiting the value of the gradients. Such results can be achieved with the help of different mathematical functions, used for neural network computing.
Why does the activation function need to be non-linear?
If we have a linear activation function, we get a model which is a linear combination of inputs. Activation functions cant be linear because such a model is effectively only 1 layer deep. Input to networks is usually linear transformation, but real-world problems are non-linear. To make the incoming data nonlinear, we use nonlinear mapping called activation functions.
Sigmoid Function:
Sigmoid function is a smooth, differentiable function that introduces non-linearity to our model. It outputs results between 0 and 1 , and used in the output layers of the DL architectures and hence used for probability-based output, and has been applied successfully in binary classification problems, modeling logistic regression tasks as well as other neural network domains. Derivative of sigmoid function is given by $\sigma(z)(1-\sigma(z))$


Sigmoid function is usually used in shallow networks because of problems like sharp damp gradients during backpropagation from hidden layers to the input layers. Sigmoid function saturates and kills the gradient, hence initializing the weights with values too big or too small can create problem. Other problems faced by sigmoid function are slow convergence, and non-zero centered output thereby causing the gradient updates to propagate in different directions.
Functions like ReLu or tangent function were proposed to remedy some of these drawbacks.
Hyperbolic Tangent Function ( tanh ):
The hyperbolic tangent function known as a tanh function, is a smooth and zero-centered function whose output lies between -1 to 1 .
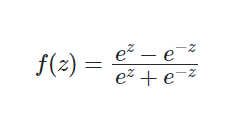
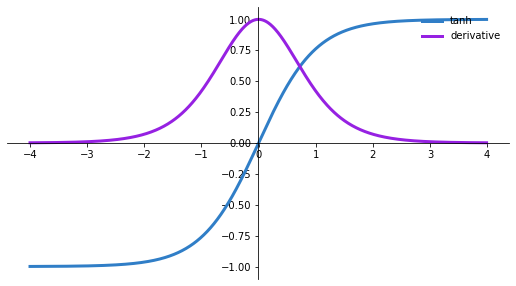 $Tanh$ function is more preferred function compared to the sigmoid function as it gives better training performance for multi-layer neural networks. $Tanh$ has a 0 centric function hence we can easily identify the values as either strongly positive, negative or neutral. It helps in centring the data and makes learning for the next layer much easier.
$Tanh$ function is more preferred function compared to the sigmoid function as it gives better training performance for multi-layer neural networks. $Tanh$ has a 0 centric function hence we can easily identify the values as either strongly positive, negative or neutral. It helps in centring the data and makes learning for the next layer much easier.
Derivative of $tanh$ is given by $ g(z)=f’(z)=(\tanh{z})^2 $,hence tanh also faces the same problem of vanishing gradient descent.
Although both sigmoid and tanh face vanishing gradient problems, tanh is zero centric, and the gradients are not restricted to move in certain directions. Therefore, in practice, tanh nonlinearity is always preferred to sigmoid nonlinearity.The tanh functions have been used mostly in recurrent neural networks for natural language processing and speech recognition tasks.
Rectified linear Activation Function:
The rectified linear activation function or ReLu function is a non-linear activation function. It returns 0 for non-positive values and "x" for any positive value "x". The graph for this function consists of two straight lines with slope 0 (for x less than )and 1(for x greater than 0). Unlike the sigmoid function its derivative is discontinuous at 0 . This creates a problem as derivative of an activation function is crucial in updating the weights after each iteration. To solve this problem, we take derivative to be 0 at x = 0 .
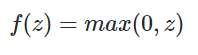
ReLu function is quite helpful in increasing the training speed of model. This is because the derivative is always either 0 or 1 for any value. This saves up a lot of time in computation during backpropagation. 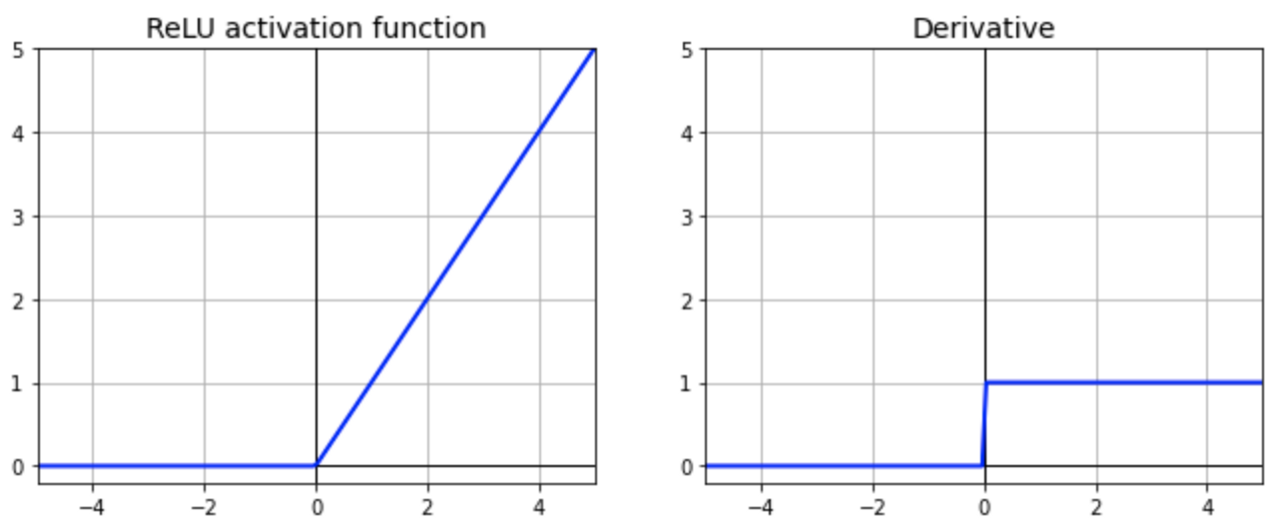 A general problem with both the sigmoid and tanh functions is that they saturate. This means that large values snap to 1.0 and small values snap to -1 or 0 for tanh and sigmoid respectively. Further, the functions are only really sensitive to changes around their mid-point of their input, such as 0.5 for sigmoid and 0.0 for tanh. ReLU adds more sensitivity to weighted sum and thus this avoids neurons from getting saturated (i.e when there is little or no variation in the output).
A general problem with both the sigmoid and tanh functions is that they saturate. This means that large values snap to 1.0 and small values snap to -1 or 0 for tanh and sigmoid respectively. Further, the functions are only really sensitive to changes around their mid-point of their input, such as 0.5 for sigmoid and 0.0 for tanh. ReLU adds more sensitivity to weighted sum and thus this avoids neurons from getting saturated (i.e when there is little or no variation in the output).
One of the problem of ReLU is the one of “dead neurons”, which occurs when the neuron gets stuck in the negative side and constantly outputs zero. Because gradient of 0 is also 0 , it’s unlikely for the neuron to ever recover. This happens when the learning rate is too high or negative bias is quite large.
Leaky ReLu:
 The Leaky ReLU activation function is just a modified form of ReLU, so to counter the disadvantages of ReLU. For the case of Leaky ReLU, it returns "x" for positive values of "x", and "a" times "x" for negative values of "x", where "a" is a parametric value. So, the gradient for positive inputs is 1, and for negative inputs, it is "a".
The Leaky ReLU activation function is just a modified form of ReLU, so to counter the disadvantages of ReLU. For the case of Leaky ReLU, it returns "x" for positive values of "x", and "a" times "x" for negative values of "x", where "a" is a parametric value. So, the gradient for positive inputs is 1, and for negative inputs, it is "a".
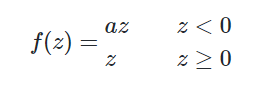
The advantage of leaky ReLU is same as that of ReLU, in addition, solving the "dead neuron" response. Now, as for negative inputs, the gradient is 'a', the neurons are able to recover with this minor modification. For choosing the value of parametric 'a', if it is very small then its learning rate will be very low and the model becomes time-consuming. So, by performing back propagation, the most appropriate value of 'a' is learnt and worked accordingly.
Softmax:
Softmax activation function is among the most popular activations functions. It is usually placed as the last layer in the deep learning model. As it is used as the last activation function of a neural network to normalize the output of a network to a probability distribution over predicted output classes.
Softmax is an activation function that scales numbers/logits into probabilities. The output of a Softmax is a vector (say v) with probabilities of each possible outcome. The probabilities in vector v sums to one for all possible outcomes or classes.
Mathematically, Softmax is defined as,
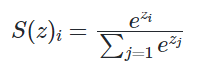 the numerator is a standard exponential function applied on $z_i$ the result is a small value(close to 0 but never 0) if $z_i$<0 and a large $z_i$ is large. A normalization term, summation of $e^{z_j}$, ensures the values of output vector sums to 1 for i-th class and each of them is in the range 0 and 1 which makes up a valid probability distribution.
the numerator is a standard exponential function applied on $z_i$ the result is a small value(close to 0 but never 0) if $z_i$<0 and a large $z_i$ is large. A normalization term, summation of $e^{z_j}$, ensures the values of output vector sums to 1 for i-th class and each of them is in the range 0 and 1 which makes up a valid probability distribution.
Or more physically it can ve observed that Softmax function calculates the probabilities distribution of the event over 'n' different events. In general way of saying, this function will calculate the probabilities of each target class over all possible target classes. Later the calculated probabilities will be helpful for determining the target class for the given inputs.